NVIDIA Jetpack Reference Guide - Comprehensive Development Insights
What is Jetpack?[1]
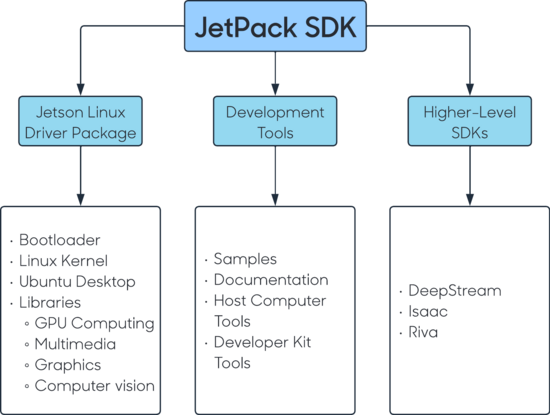
This Software Development Kit (SDK) is a comprehensive solution for building AI applications. JetPack SDK provides a full development environment for hardware-accelerated AI-at-the-edge development. JetPack SDK includes Jetson Linux Driver Package with bootloader, Linux kernel, Ubuntu desktop environment, and a complete set of libraries for acceleration of GPU computing, multimedia, graphics, and computer vision.
It also includes samples, documentation, and developer tools for both the host computer and the developer kit and supports higher level SDKs such as DeepStream for streaming video analytics, Isaac for robotics, and Riva for conversational AI.
Why use Jetpack?
NVIDIA Jetpack is a powerful toolkit designed to fully utilize Jetson platforms. It’s ideal for building:
- AI-powered robots
- Advanced computer vision applications
- Sophisticated edge devices
Benefits of Jetpack
- Optimized Performance for AI and Deep Learning: Jetpack leverages GPU-accelerated capabilities like CUDA and TensorRT, enabling real-time execution of complex computations. This makes it perfect for applications requiring real-time performance.
- Unified Development Experience: Develop an application once and easily scale, adapt, and deploy it across different Jetson modules. This ensures flexibility and reusability across the Jetson family.
- Extensive Ecosystem: Jetpack supports a wide range of libraries, frameworks, and community-driven resources, making it easier to start and grow your projects. Compatibility with industry-standard AI and robotics frameworks like ROS also simplifies integration and speeds up time to market.
Main Features
Libraries
NVIDIA Jetpack includes several libraries for applications in deep learning, GPU accelerated applications, and computer vision. These libraries includes:
- TensorRT: A high-performance deep learning inference runtime for image classification, segmentation, and object detection neural networks. It speeds up deep learning inference as well as reducing the runtime memory footprint for convolutional and deconv neural networks.
- CUDA-X: A set of libraries that deliver higher performance compared to CPU-only alternatives across application domains, including AI and high-performance computing. Some of these libraries includes:
- CUDA Math Libraries
- Parallel Algorithm Libraries
- Data Processing Libraries
- Communication Libraries
- Quantum Libraries
- Partner Libraries
- Computational Lithography
- Image and Video Libraries
- Deep Learning Core
- CUDA Deep Neural Network (CuDNN): Is a library that provides high-performance primitives for deep learning frameworks. It includes support for convolutions, activation functions, and tensor transformations.
- Multimedia API: The Jetson Multimedia API package provides low level APIs for flexible application development.
- Camera application API: libargus offers a low-level frame-synchronous API for camera applications, with per frame camera parameter control, multiple (including synchronized) camera support, and EGL stream outputs.
- Sensor driver API: V4L2 framework enables video decode, encode, format conversion, and scaling functionality. V4L2 for encoding opens up many features like bit rate control, quality presets, low latency encoding, temporal tradeoff, motion vector maps, and more.
- Vision Programming Interface (VPI): Is a software library that provides Computer Vision / Image Processing algorithms implemented on PVA (Programmable Vision Accelerator), GPU and CPU.
- OpenCV: Open source library for computer vision, image processing, and machine learning, and now features GPU acceleration for real-time operation.
Developer Tools
NVIDIA JetPack offers developer tools for application development, debugging, profiling, and optimization. Some of these tools are used directly on the Jetson system, while others run on a Linux host computer connected to the Jetson system. These tools are:
- NVIDIA Nsight Eclipse Edition: Is a full-featured IDE powered by the Eclipse platform. It provides an all-in-one integrated environment to edit, cross-compile, and debug CUDA-C applications.
- CUDA-GDB: Is a command line tool bundled with CUDA Toolkit that delivers a seamless debugging experience, allowing you to debug both the CPU and GPU portions of your application simultaneously.
- CUDA-MEMCHECK: Is a command line tool bundled with CUDA Toolkit that detects the source and cause of memory access errors in your GPU code. It also reports runtime execution errors, identifying situations that could otherwise result in an “unspecified launch failure” error when your application is running.
- NVIDIA Nsight Systems: is a low overhead system-wide profiling tool, providing the insights developers need to analyze and optimize software performance. It uses GPU tracing, CPU sampling and tracing, and OS thread state tracing to visualize an application’s algorithms.
- nvprof: Is a command line tool bundled with CUDA Toolkit that enables you to collect and view profiling data, i.e., a timeline of CUDA-related activities on both CPU and GPU.
- NVIDIA Nsight Graphics: Is a standalone application for debugging and profiling graphics applications. Powerful analysis tools help identify optimization opportunities. Runs on a Linux host computer.
- NVIDIA Nsight Compute: Is an interactive kernel profiler for CUDA applications. It provides detailed performance metrics for analysis and enables results comparison between baselines and the current run.
- NVIDIA Nsight Deep Learning Designer: An integrated development environment that helps developers efficiently design and develop deep neural networks for in-app inference.
- NVIDIA Nsight Compute CLI: Provides a non-interactive way to profile applications from the command line. It can print the results directly on the command line or store them in a report file.
References



