GStreamer Pan Tilt Zoom and Rotate Element - Zoom
| GStreamer PTZR |
|---|
 |
| GstPTZR Basics |
| User Guide |
| Getting Started |
| Examples |
| Contact Us |
This page serves as a reference on how to adjust zoom values on GstPTZR.
Zoom Levels
The zoom effect is achieved by taking a capture region of different sizes, and scaling it to the output size. Taking a smaller capture region, will require an upscale and pixel interpolation, achieving the zoom in effect. On the other hand, taking a bigger capture region will require a downscale, hence, the zoom out effect. The following sections describe in more detail each zoom configuration. To do so, the following standard is used:
- in-size
- The size of the input image
- out-size
- The size of the output image
- zoom-level
- The value currently configured in the zoom
zoom-level = 1
When zoom-level is set to 1, there is no magnification expected. Hence, a region of size out-size will be taken from the input image. No scaling is required to fit the capture region in the output image, since both match out-size. Figure 1 exemplifies this concept.

0 <= zoom-level < 1
For values lesser than 1, zoom-level can take real values starting from 0. This limit value of 0 represents the biggest capture region that fits in the input image while maintaining the output image's aspect ratio. Figure 2 shows graphically this concept. For values in between 0 and 1, the capture region will vary accordingly. Note that, in this case, a downscale of the capture region is perform to fit out-size.

zoom-level > 1
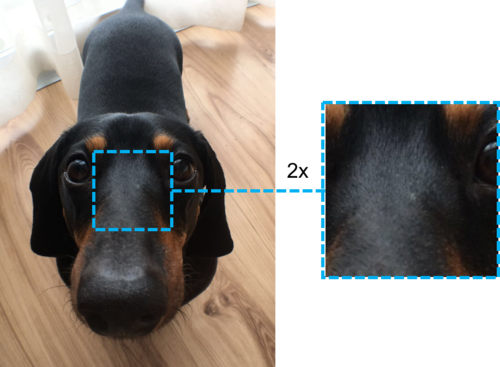
For values greater than 1, zoom-level is taken literally as a multiplication factor. For example, for a value of 2, half out-size is taken and upscaled. Internally, OpenGL will interpolate the pixels. The only upper bound defined to the zoom is for the case that the capture region is a single pixel. Figure 3 exemplifies this concept.