Robot Operating System ROS on Jetson Platforms

|
|
Introduction
The Robot Operating System (ROS) is a flexible framework for writing robot software. It is a collection of tools, libraries, and conventions that aim to simplify the task of creating complex and robust robot behavior across a wide variety of robotic platforms.
Why? Because creating truly robust, general-purpose robot software is hard. From the robot's perspective, problems that seem trivial to humans often vary wildly between instances of tasks and environments. Dealing with these variations is so hard that no single individual, laboratory, or institution can hope to do it on their own.
As a result, ROS was built from the ground up to encourage collaborative robotics software development. For example, one laboratory might have experts in mapping indoor environments, and could contribute a world-class system for producing maps. Another group might have experts at using maps to navigate, and yet another group might have discovered a computer vision approach that works well for recognizing small objects in clutter. ROS was designed specifically for groups like these to collaborate and build upon each other's work, as is described throughout this site.
Installation
The following installation steps were tested on a Jetson TX2 and Jetson Nano, but should apply to any Jetson Platform (Xavier, Xavier NX) or Desktop Computers with Ubuntu.
Configure packages sources
sudo sh -c 'echo "deb http://packages.ros.org/ros/ubuntu $(lsb_release -sc) main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ros-latest.list' sudo apt-key adv --keyserver 'hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80' --recv-key C1CF6E31E6BADE8868B172B4F42ED6FBAB17C654 sudo apt update
Install ROS from packages
You can choose from one of the following options:
1.Desktop-Full Install (Recommended): ROS, rqt, rviz, robot-generic libraries, 2D/3D simulators and 2D/3D perception
sudo apt install ros-melodic-desktop-full
2.Desktop Install: ROS, rqt, rviz, and robot-generic libraries
sudo apt install ros-melodic-desktop
3.ROS-Base: (Bare Bones): ROS package, build, and communication libraries. No GUI tools.
sudo apt install ros-melodic-ros-base
To find available packages, use:
apt search ros-melodic
Configure ROS
Before you can use ROS, you will need to initialize rosdep. rosdep enables you to easily install system dependencies for source you want to compile and is required to run some core components in ROS.
To install ROS initializer:
sudo apt-get install python-rosdep -y sudo apt-get install python-rosinstall python-rosinstall-generator python-wstool build-essential -y sudo c_rehash /etc/ssl/certs
Then execute:
sudo rosdep init rosdep update
Environment Setup
It's convenient if the ROS environment variables are automatically added to your bash session every time a new shell is launched:
echo "source /opt/ros/melodic/setup.bash" >> ~/.bashrc source ~/.bashrc
Execute ROS
You will need to launch ROS process from a terminal:
roscore
Which will generate an output similar to the following:
nvidia@nvidia-desktop:~$ roscore ... logging to /home/nvidia/.ros/log/5ee9868e-6a1f-11ea-b91d-00044bf25e44/roslaunch-nvidia-desktop-20965.log Checking log directory for disk usage. This may take a while. Press Ctrl-C to interrupt Done checking log file disk usage. Usage is <1GB. started roslaunch server http://nvidia-desktop:39719/ ros_comm version 1.14.4 SUMMARY ======== PARAMETERS * /rosdistro: melodic * /rosversion: 1.14.4 NODES auto-starting new master process[master]: started with pid [20976] ROS_MASTER_URI=http://nvidia-desktop:11311/ setting /run_id to 5ee9868e-6a1f-11ea-b91d-00044bf25e44 process[rosout-1]: started with pid [20987] started core service [/rosout]
To verify ros was correctly launched, from another terminal, while keeping the last one opened, you can run rosnode list
nvidia@nvidia-desktop:~$ rosnode list /rosout
Intel RealSense Camera Support
Installation
For the melodic ROS distribution
sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-realsense2-camera
Default resolution may not be configured, you can check video format and size with
v4l2-ctl --device /dev/video3 --list-formats-ext
Apply correct settings to all available modes at:
sudo vim /opt/ros/melodic/share/realsense2_camera/launch/rs_camera.launch
For example for depth mode, introduce correct width and height and true to enable camera stream:
... <arg name="depth_width" default="480"/> <arg name="depth_height" default="270"/> <arg name="enable_depth" default="true"/> ...
Install ROS Visualizer
sudo apt-get install rviz
Start Camera Streaming
To use the camera with ROS, you will need to execute 3 processes, to ease the steps using terminator is recommended.
1. Run ROS core
roscore
2. Run ROS visualizer
rviz
3. Run ROS realsense camera
roslaunch realsense2_camera rs_camera.launch filters:=pointcloud
As follows:

Use RVisualizer
On the Visualizer
1. Click the Add button to add a new source

2. Click the By topic tab, and then DepthCould . Repeat to also add Image.
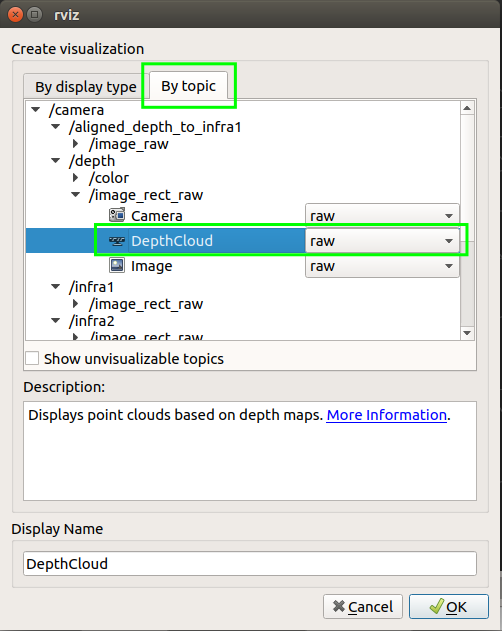
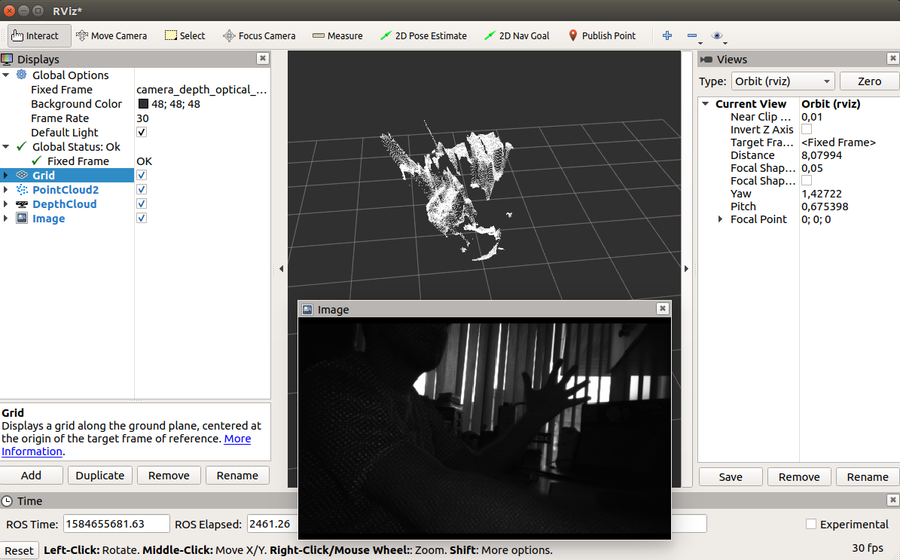
3. You will get a view similar to the following
Use IntelRealsense Visualizer
The IntelRealsense library also includes its own visualization tool, that can be executed with:
realsense-viewer
Some configurations can be seen in the following image:
[1] Add source: if the camera is not detected by default, please try to disconnect and reconnect it to the usb port and click this button.
[2] On/off click this button to enable/disable camera streams.
[3] Stream settings Select required resolution and framerate.
[4] Select streams Choose the streams to be displayed.
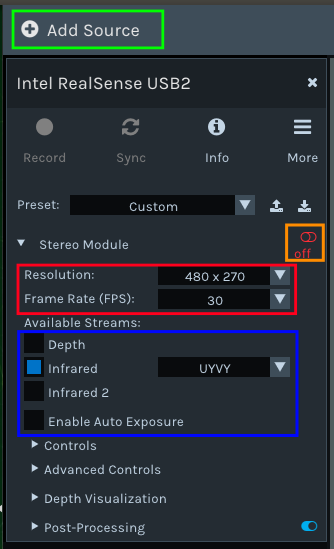
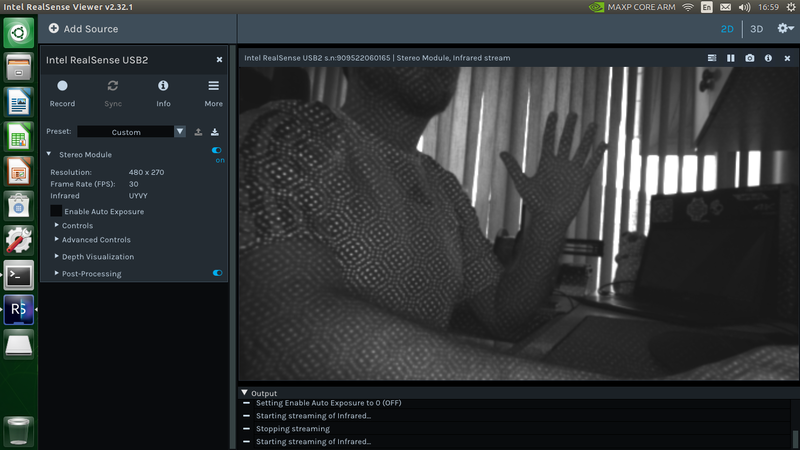
For example with a single infrared stream you will get the following output:
For direct inquiries, please refer to the contact information available on our Contact page. Alternatively, you may complete and submit the form provided at the same link. We will respond to your request at our earliest opportunity.
Links to RidgeRun Resources and RidgeRun Artificial Intelligence Solutions can be found in the footer below.

