Error Handling with the Single Input Single Output Pattern
Introduction
This wiki page presents the Single Input Single Output programming pattern. It gives context on why is it necessary, how to use it with examples, explains the use of the goto statement and why is it a useful tool in this case along with considerations about the use of it, and finally, the reason we don't use the SISO pattern in C++.
What is the SISO pattern?
- The Single Input Single Output is a pattern for procedural C code.
- It is based on the idea that a function should have a single entry point and a single output point.
- It assists in the task of error handling in a way that makes it easy, and scalable, avoids code duplication, and keeps the code clean.
- The SISO pattern makes use of the goto statement to accomplish its purpose.
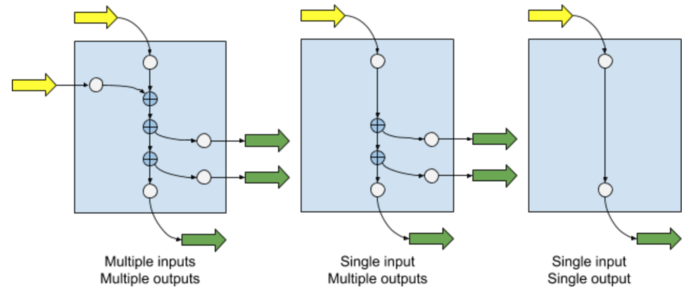
Error Management
When using a programming language like C, it is often needed to have to think about how are error going to be managed in programs. Error management becomes increasingly more complicated when there is allocated memory or/and handles in different parts of the program. Usually the resources are freed right before the function or program finishes, but if exiting early from the program or function is required, then this would mean those resources need to be freed right before exiting as well. This can be tricky since if the memory is not liberated before returning, a memory leak will be produced.
The next sections present some examples and ways to handle this.
Code duplication
A way to perform error management in C is to have consecutive if cases that check for errors and for each error case and returns, freeing the resources before returning. This will get more messy every time a new resource is needed. This procedure entails that the same code will need to be replicated for error case and the function has multiple outputs.
Take for example the next piece of code. For each error encountered and handled, the amount of resources needed to be freed increases, and it is very hard to keep track of all of them. It also makes it non-scalable over time, imagine if this code needs to be changed in a way that another early return is needed do to some condition failing, that person would have to study the code carefully to avoid leaving behind unfreed resources. Even more, needed to change the clean up code in general would mean that the person would need to go through all the function and make sure all the code was correctly modified in all the clean up cases. All of these remarks make this way of error handling not recommend, since leaving behind memory leaks will become very likely.
int main()
{
FILE *my_reading_file = NULL;
FILE *my_writing_file = NULL;
int *int_array = NULL;
int error = 0;
int ret_val = 0;
my_reading_file = fopen("input.txt", "r");
if (my_reading_file == NULL) {
ret_val = 1;
return ret_val;
}
/* Int array of size 4 */
int_array = malloc(4 * sizeof(int));
if (!int_array) {
fclose(my_reading_file);
ret_val = 1;
return ret_val;
}
my_writing_file = fopen("output.txt", "w");
if (my_writing_file == NULL) {
fclose(my_reading_file);
free(int_array);
int_array = NULL;
ret_val = 1;
return ret_val;
}
error = example_function(0);
if (error) {
fclose(my_reading_file);
fclose(my_writing_file);
free(int_array);
ret_val = 1;
return ret_val;
}
/* ... More code ... */
printf("This code is going as planned!\n");
printf("More text printed!\n");
fclose(my_reading_file);
fclose(my_writing_file);
free(int_array);
return ret_val;
}
Nested ifs
A way to avoid having duplicated code to free sources is to use nested if/else blocks that allow the program to exit and clean up resources properly.
Take for example the next piece of code. The error is evaluated at assignment and resources will be freed when an error is caught. This makes this code free of any code duplication. Notice as well that the function now has one single output. This kind of error management can be recommended when the number of resources is small.
int main()
{
FILE *my_reading_file = NULL;
int *int_array = NULL;
int ret_val = 0;
if (my_reading_file = fopen("input.txt", "r") != NULL) {
/* ... More code ... */
if (int_array = malloc(4 * sizeof(int)) != NULL) {
/* ... More code ... */
free(int_array);
int_array = NULL;
} else {
ret_val = 1;
}
fclose(my_reading_file);
} else {
ret_val = 1;
}
return ret_val;
}
This approach however, can become harder to manage for every new resource to be added very quickly. Take for example the next piece of code. With 4 resources to manage, it is clear how the code becomes really tangled and hard to read, which adds a ton of complexity. Changing the clean up logic would mean having to study the code until finding the specific condition that does it. This makes this approach really non-scalable as well.
int main()
{
FILE *my_reading_file = NULL;
FILE *my_writing_file = NULL;
int *int_array = NULL;
int ret_val = 0;
if ((my_reading_file = fopen("input.txt", "r")) != NULL) {
/* ... More code ... */
if ((int_array = malloc(4 * sizeof(int))) != NULL) {
/* ... More code ... */
if ((my_writing_file = fopen("output.txt", "w")) != NULL) {
/* ... More code ... */
if (example_function(0) != 1) {
/* ... More code ... */
} else {
ret_val = 1;
}
fclose(my_writing_file);
} else {
ret_val = 1;
}
free(int_array);
int_array = NULL;
} else {
ret_val = 1;
}
fclose(my_reading_file);
} else {
ret_val = 1;
}
return ret_val;
}
Clean up functions
Another approach to be sure that resources are freed correctly is to use GCC's variable attributes. The keyword __attribute__ allows specification of special properties of variables. In this case, the attribute of interest would be the cleanup attribute. This allows a callback function to be called when the variable goes out of scope, this function would then free the variable's resources.
Two steps need to be done to have the described behavior.
1. The cleanup callback function must be defined.
2. The variable needs to be declared in a specific way:
__attribute__((cleanup(<callback function>))) <type> <variable_name>;
The following example demonstrates the use of these variable attributes. The downside to this is that the code would need to be changed in two different places when more resources need to be allocated (as well needing to review the cleanup functions already defined to avoid defining unnecessary ones and avoid code repetition), as well as always having to keep in mind to initialize variables with the special syntax so a cleanup function is attached to them. As you can see, this also hinders code readability and does not look clean at all.
void free_int_array(int **value)
{
free(*value);
}
void close_file(FILE ** file)
{
fclose(*file);
}
int main()
{
__attribute__ ((cleanup(close_file))) FILE *my_reading_file = NULL;
__attribute__ ((cleanup(close_file))) FILE *my_writing_file = NULL;
__attribute__ ((cleanup(free_int_array))) int *int_array = NULL;
int error = 0;
my_reading_file = fopen("input.txt", "r");
if (my_reading_file == NULL) {
return 1;
}
/* Int array of size 4 */
int_array = malloc(4 * sizeof(int));
if (!int_array) {
return 1;
}
my_writing_file = fopen("output.txt", "w");
if (my_writing_file == NULL) {
return 1;
}
error = example_function(1);
if (error) {
return 1;
}
/* ... More code ... */
printf("This code is going as planned!\n");
printf("More text printed!\n");
return 0;
}
Introduction to SISO
We can make use of the goto statements to create the SISO pattern, also called goto chain.
With the SISO pattern, we will write only one "destroy" statement for each "create" statement. In this case, we are using "create" and "destroy" in a very vague way, since it can be anything from a malloc/free pair, to a lock/unlock of a mutex.
Goto
The goto statement is not recommended for most use cases, but in very specific exceptions it can be useful and recommended to use. One of these exceptional use cases is precisely to be able to handle errors in a controlled, simple and readable-friendly way, the goto statement is only used to transfer control within a single function. Take the code below as an example. Notice that all the downsides of the past approaches for error management are now solved:
- The freeing of each resource is done only once at the end of the function.
- The code is simple enough that adding and freeing a new resource is easy and the code to be modified is contained, thus making the code scalable.
- The code is kept clean and easy to read.
This approach takes an important part in the Single Input Single Output pattern. The next sections explain in more detail how to apply this pattern using this goto statement approach for error management.
int main()
{
FILE *my_reading_file = NULL;
FILE *my_writing_file = NULL;
int *int_array = NULL;
int error = 0;
int ret_val = 0;
my_reading_file = fopen("input.txt", "r");
if (my_reading_file == NULL) {
ret_val = 1;
goto FAIL_RFILE;
}
/* Int array of size 4 */
int_array = malloc(4 * sizeof(int));
if (!int_array) {
ret_val = 1;
goto CLOSE_RFILE;
}
my_writing_file = fopen("output.txt", "w");
if (my_writing_file == NULL) {
ret_val = 1;
goto FREE_ARR;
}
error = example_function(0);
if (error) {
ret_val = 1;
goto CLOSE_WFILE;
}
/* ... More code ... */
printf("This code is going as planned!\n");
printf("More text printed!\n");
CLOSE_WFILE:
fclose(my_writing_file);
FREE_ARR:
free(int_array);
int_array = NULL;
CLOSE_RFILE:
fclose(my_reading_file);
FAIL_RFILE:
return ret_val;
}
How to apply the SISO pattern
The following example follows the SISO pattern. You can observe that there's only one free statement in the code for each memory allocation, and all that we do is jump to the required free logic when needed (for example on errors).
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int *x = NULL;
int *y = NULL;
int ret = 0;
x = (int*) malloc(sizeof(int));
if (!x) {
ret = 1;
goto out;
}
y = (int*) malloc(sizeof(int));
if (!y) {
ret = 1;
goto free_x;
}
free (y);
free_x:
free (x);
out:
return ret;
}
The importance of this method is that, as soon as we jump to a label with a goto, the logic beneath will also be executed. So this is really a chain, if you jump to free_x, then the logic under out will also be executed (which is what we want).
Code symmetry
The SISO pattern is totally symmetric. If you block/allocate resources in the XYZ order, the SISO pattern will make sure to unblock/deallocate the same resources in the opposite order (ZYX). This will help automate the cases when, for example, the execution flow doesn't reach the Z step, so we just jump to the label that starts the unblock/deallocate logic of Y. This is because, since we know Z was never a thing, then we don't need to undo anything related to Z.
Hopefully, the examples below will make sense of all the explanations.
Examples
SISO
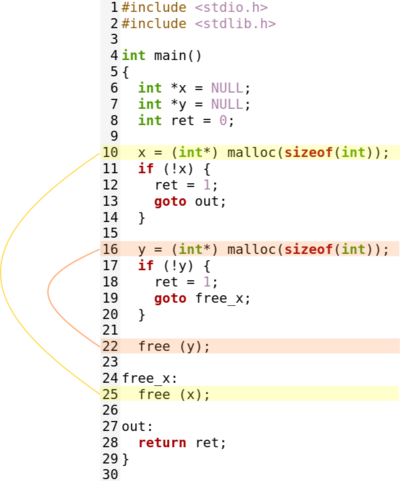
The image below shows very explicitly a SISO pattern with 2 resources.
The idea here is to free the resources when detecting an error. But only the resources that were actually created need to be freed (otherwise we will get a segfault).
In this example, we do not need to free X if there was no memory to create it (so we just jump to the out label and return). But, if X was created but it's not the case for Y, we also need to return, but just after freeing X, so we need to jump to free_x instead of goto.
The beauty of the SISO pattern comes when we need to scale the functionality. Let's say that we are working on a feature where we need to allocate a third resource called z. The nature of the SISO pattern will let us just add literally the allocation and a new label to free the resource on demand, as can be seen in the figure below.
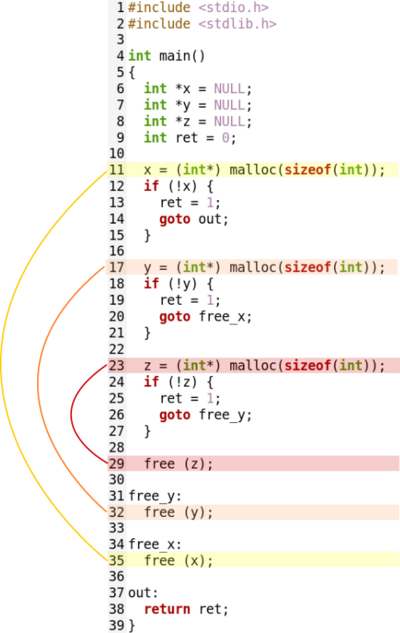
Again, by keeping the symmetry, a big refactor was not required in order to extend the code. Now take a minute to think what would have happened if we were following the Single Input Multiple Output pattern instead.
goto Dangers
The goto statement is not recommended for most use cases! Using goto should be used only in controlled and contained manners with a specific purpose, like transferring control withing a function to handle errors. Using goto as a programming practice is just a ticking bomb for disaster.
Here are some reasons as to why the goto statement should be avoided:
- The use of goto makes the code very confusing. It makes it really difficult to trace the program flow, thus making the program really hard to understand. In his famous paper about the use of goto statement, Dijkstra's main argument is that it should be obvious what the program does from looking at it, and that it would not be the case by using the
gotostatement. - Confusing and not understandable code is a recipe for disaster. Adding more code to tangled code makes the code even more tangled, and tangled code is impossible to maintain.
- Tangled code does not only make the code horrible to work on, it also makes it extremely hard to debug. Debugging is already a challenge, now imagine trying to debug a program that jumps around constantly and without structure.
For this, goto should only be used when the code would be benefited from it, which is in very exceptional cases.
"Unconditional branching is a tool. Some tools, such as chainsaws, are dangerous. We don’t want people running around recklessly swinging chainsaws everywhere. This does not mean that chainsaws should be banned. There are situations where careful use of a chainsaw is the best choice." (Don Cross, 2020)
Why is the SISO pattern not used in C++?
The SISO pattern does not make sense in C++. In C++, programmers are able to use objects that manage their own resources, so he / she does not need to worry about allocating them or releasing them later. This kind of practice is called RAII.
Use of RAII in C++
RAII stands for Resource Acquisition Is Initialization. Using RAII, the resources needed for the object are acquired and created when the object is initialized and freed when the object is destroyed. This way, all heap allocated resources or any object handles will be owned by a stack-allocated object, so when this object goes out of scope, its destructor will have the code to take care of the resourced previously allocated or consequent clean up code.
Fortunately, C++'s Standard Library provides a lot of containers that follow RAII. A C++ programmer should always use objects that follow RAII rather than allocating resources manually.
This all means that several output functions are not a problem, since resources are managed by the objects themselves. Error management a lot easier as well if used correctly.
Tips
When using C++ always try to follow these tips:
- Try to avoid using pointers if possible. If you need to modify a variable in a function, it is better to pass said variable as a reference.
- Use RAII containers if possible. For example you can use a std::vector instead of an array, a std::string instead of a char* and so on. This way you won't have to worry about the memory that was allocated for these, as these RAII containers handle memory by themselves.
- If you do need pointers, like for example when using a third party framework, make sure to use pointer wrappers like smart pointers.
class RRObject {
public:
void DoSomething(){}
};
void my_example_function (std::unique_ptr<RRObject> myObj) {
/* Some code */
}
int main () {
{
std::unique_ptr<RRObject> myObj(new RRObject());
// Access attributes normally
myObj->DoSomething();
// Dereference normally
my_example_function(myObj);
}
References
- MEM12-C. Consider using a goto chain when leaving a function on error when using and releasing resources
- Using the __cleanup__ variable attribute in GCC
- Go to statement considered harmful
- Is Goto Always Evil?
- RAII
Contact Us
For direct inquiries, please refer to the contact information available on our Contact page. Alternatively, you may complete and submit the form provided at the same link. We will respond to your request at our earliest opportunity.
Links to RidgeRun Resources and RidgeRun Artificial Intelligence Solutions can be found in the footer below.

