RidgeRun Yocto Developer Guide/Introduction: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<noinclude> | <noinclude> | ||
{{RidgeRun Yocto Developer Guide/Head | {{RidgeRun Yocto Developer Guide/Head | ||
|previous=https://developer.ridgerun.com/wiki/index.php/RidgeRun_Yocto_Developer_Guide | |previous=https://developer.ridgerun.com/wiki/index.php/RidgeRun_Yocto_Developer_Guide | ||
|next=https://developer.ridgerun.com/wiki/index.php/RidgeRun_Yocto_Developer_Guide/RidgeRun_Services_and_Development | |next=https://developer.ridgerun.com/wiki/index.php/RidgeRun_Yocto_Developer_Guide/RidgeRun_Services_and_Development}} | ||
}} | |||
</noinclude> | </noinclude> | ||
| Line 11: | Line 10: | ||
== Introducing Yocto == | == Introducing Yocto == | ||
One of the | One of the biggest challenges in embedded systems development is to adapt a complete operating system to the project needs. The [https://www.yoctoproject.org/ Yocto Project] emerges as a powerful tool set designed to streamline the creation of custom Linux distributions for embedded devices. Key features include its extensive support for a wide range of hardware platforms, ensuring compatibility across diverse embedded devices. | ||
[[File: | [[File:Screenshot from 2024-09-27 09-40-18.png|450px|thumb|center|alt=Chart describing advantages and disadvantages to use Yocto.]] | ||
=== What is Yocto? === | === What is Yocto? === | ||
Yocto is an open-source collaboration project that provides templates, tools, and methods to help create custom Linux distributions for embedded systems. It enables developers to build and maintain their own Linux distributions tailored specifically to the unique requirements of their embedded devices. | |||
Yocto is essentially composed by a framework | Yocto is essentially composed by a framework called OpenEmbedded. This framework utilizes metadata, in the form of recipes, to specify how software packages should be built and integrated into the Linux distribution. Recipes are then organized in layers, which allow for modularity and customization. | ||
[[File:Yocto comp.png|650px|thumb|center]] | [[File:Yocto comp.png|650px|thumb|center|alt=image describing the different components of Yocto Project]] | ||
* '''Yocto''' | * '''Yocto Project''' coordinates and manages the overall framework for creating custom Linux distributions. | ||
* '''Poky''' is the specific implementation and reference build system within the Yocto Project, incorporating BitBake and OpenEmbedded. | * '''Poky''' is the specific implementation and reference build system within the Yocto Project, incorporating BitBake and OpenEmbedded. | ||
| Line 39: | Line 38: | ||
=== Why do we use Yocto? === | === Why do we use Yocto? === | ||
Yocto | Yocto can be used in any specific project involving embedded systems. However, there are some particular scenarios where Yocto is the best option. | ||
# ''' | # '''Custom Requirements''': When the embedded device used needs a highly customized Linux distribution to satisfy the conditions. Yocto allows the developer to select, configure, and integrate all and only the necessary components and features to optimize performance, resources and functionality. | ||
#: | #: | ||
# '''Hardware Diversity''': When the embedded system involves the use of multiple hardware platforms or | # '''Hardware Diversity''': When the embedded system involves the use of multiple hardware platforms or requires a very specific hardware configuration. Yocto is able to handle multiple architectures and adapt its characteristics to each platform. | ||
#: | #: | ||
# '''Reproducibility and Scalability''': Yocto is designed for reproducibility and scalability. By defining software configurations and dependencies in recipes and layers, developers can reliably reproduce builds across different environments and scale their projects from prototypes to production-ready systems. | # '''Reproducibility and Scalability''': Yocto is designed for reproducibility and scalability. By defining software configurations and dependencies in recipes and layers, developers can reliably reproduce builds across different environments and scale their projects from prototypes to production-ready systems. | ||
Latest revision as of 20:26, 4 October 2024
Introducing Yocto
One of the biggest challenges in embedded systems development is to adapt a complete operating system to the project needs. The Yocto Project emerges as a powerful tool set designed to streamline the creation of custom Linux distributions for embedded devices. Key features include its extensive support for a wide range of hardware platforms, ensuring compatibility across diverse embedded devices.
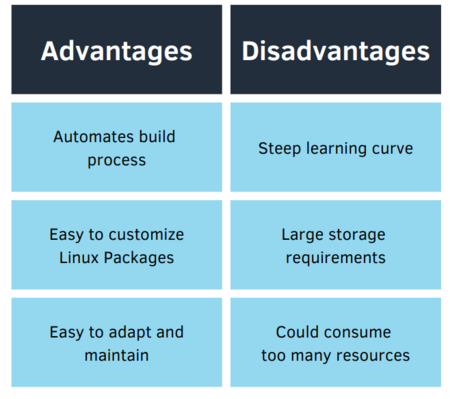
What is Yocto?
Yocto is an open-source collaboration project that provides templates, tools, and methods to help create custom Linux distributions for embedded systems. It enables developers to build and maintain their own Linux distributions tailored specifically to the unique requirements of their embedded devices.
Yocto is essentially composed by a framework called OpenEmbedded. This framework utilizes metadata, in the form of recipes, to specify how software packages should be built and integrated into the Linux distribution. Recipes are then organized in layers, which allow for modularity and customization.
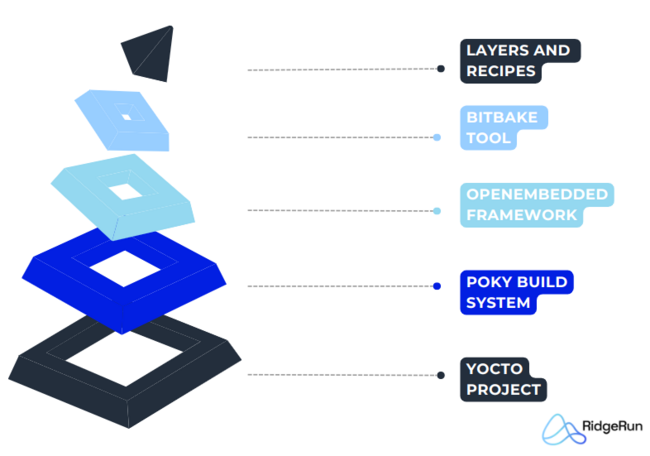
- Yocto Project coordinates and manages the overall framework for creating custom Linux distributions.
- Poky is the specific implementation and reference build system within the Yocto Project, incorporating BitBake and OpenEmbedded.
- OpenEmbedded provides the foundational build framework and essential recipes for constructing Linux distributions.
- BitBake executes tasks defined in recipes, managing the build process from dependency resolution to final image generation.
- Layers allow developers to modularly add and customize components and configurations, facilitating flexibility and reuse.
- Recipes define the specifics of how individual software packages are built, ensuring consistency and reproducibility across different projects and environments.
If you want to learn more about Yocto concepts you can refer to Yocto Main Concepts.
Why do we use Yocto?
Yocto can be used in any specific project involving embedded systems. However, there are some particular scenarios where Yocto is the best option.
- Custom Requirements: When the embedded device used needs a highly customized Linux distribution to satisfy the conditions. Yocto allows the developer to select, configure, and integrate all and only the necessary components and features to optimize performance, resources and functionality.
- Hardware Diversity: When the embedded system involves the use of multiple hardware platforms or requires a very specific hardware configuration. Yocto is able to handle multiple architectures and adapt its characteristics to each platform.
- Reproducibility and Scalability: Yocto is designed for reproducibility and scalability. By defining software configurations and dependencies in recipes and layers, developers can reliably reproduce builds across different environments and scale their projects from prototypes to production-ready systems.
- Support and Maintenance: For projects requiring long-term support and maintenance, Yocto provides a structured methodology for managing dependencies, updates, and patches.

