RidgeRun Engagement Analytics Microservice

RidgeRun's Engagement Analytics Service is in charge of managing people engagement statistics. It reads detection/direction messages from Redis and based on the given configuration it calculates the person engagement and then posts statistics in both Redis and InfluxDB. It also calculates a heatmap of engaged people's locations and posts it as a redis stream.
The following picture shows a basic diagram of the service
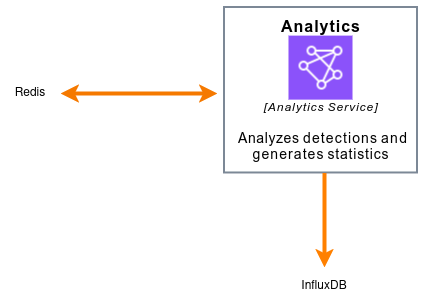
The service can be configured using a configuration file or via REST API.
Service Configuration
The service can be configured in 2 different ways: providing a configuration file via the --config-file CLI argument or via the /configuration request (see the [service API documentation]). In both cases, the configuration will be in JSON format as follows:
{
"heatmap": {
"window_seconds": 3600,
"eps": 40,
"min_samples": 2,
"update_period": 10
},
"engagement": [
{
"id": "cam0",
"roi": [
{
"x": 0,
"y": 1079
},
{
"x": 1919,
"y": 1079
}
]
},
{
"id": "cam1",
"roi": [
{
"x": 0,
"y": 1079
},
{
"x": 1919,
"y": 1079
}
]
}
],
"db_update_period": 5,
"message_expiration": 5
}
The configuration entries are as follows:
- heatmap: This is the configuration for the heatmap generation.
- window_seconds: This is the window of time that will be used for the heatmap generation. Any sample older than this time will be discarded.
- eps: This is the maximum distance between 2 samples to be considered part of the same group.
- min_samples: This is the minimum number of samples in a group to be considered. Any group with less that this number of samples will be discarded.
- update_period: This is the period used to generate and update the heatmap. Data will be constantly collected but the heatmap will be calculated and posted in redis with this period in seconds.
- engagement: This is the data for engagement calculation. It is an array with one element per camera.
- id: The id of the camera.
- roi: This is the target region for the engagement. Any person whose direction points to this defined region is considered to be engaged. It supports 1 or 2 points. In case of one point, the person is considered to be engaged if it is looking at that point. In case of 2 points, the person is considered to be engaged if it is looking at the rect defined by the 2 points.
- db_update_period: This is the period of time used to update the influx database with statistics.
- message_expiration: This is the amount of seconds used for engagement messages expiration. If a person is not seen for this configured amount of time, the entry will automatically disappear from redis.
Statistics
The service reads detection/direction statistics from redis with the following format:
{
"id": 1,
"cameraid": "cam1",
"timestamp": "2025-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"width": 1920,
"height": 1080,
"detections": [
{
"objectid": "object1",
"position": {
"x": 10,
"y": 20
},
"direction": {
"x": 1,
"y": 0
}
}
]
}
The detections field is an array with the object ID, its position and its direction vector.
With this information, the services is constantly generating the following statistics:
- Redis:
- Engagement: This is a redis message with key <personid>:engagement and content {engaged:<int 0/1 indicating if the person is engaged>, engagement:<engagement in seconds>,"last-seen":. The messages are posted in redis with an expiration time (message_expiration field in configuration) so they will disappear if not updated (the person hasn't been seen) for the given time.
- Heatmap: Heatmap of engaged people over a configrable period of time (heatmap->window_seconfs in configuration). This message uses the HeatmapSchemaGenerator from rrms-utils and has the following format: "heatmap":[{"position":{"x":int, "y": int}, "intensity":float, "radius": int}, {"position":{"x":int, "y": int}, "intensity":float, "radius": int}, ...]
- InfluxDB: InfluxDB is used for the data monitoring service so here is where the monitored statistics are posted. All influx data is stored in a bucket called jetson_metrics in Ridgerun organization. The following data is stored:
- engagement_metrics: This is a measurement used to store the following engagement related metrics:
- detected_people: The amount of people that has been detected.
- total_engaged_people: The amount of people that has been engaged.
- total_engagement: The total amount of engagement in seconds.
- total_seconds: The amount of seconds the service has been running collecting statistics.
- Engaged persons: This measurement is used to report the amount of persons engaged per hour. It used the following field: {persons: <number of persons>}
- Engagement: This measurement is used to report 2 statistics using 2 different tags: average to report the average engagement and by hour to report the engagement per hour. The engagement is reported in a filed {engagement: <engagement time in seconds>}
- Real Time: This measurement is used to report real time data. The data is collected in a window of time equals to db_update_period in configutation. It has the following fields:
- detected_people: Amount of unique persons detected in the time window.
- engaged_people: Amount of people engaged in the time window.
- engagement_time: The total engagement time in the time window. This is, the sum of the engagement time of all the engaged people.
- person_id: This field is used to report the detected IDs. It is sent with the detections tag if it is a regular detection (not engaged) and with the engaged tag if the id is engaged.
- engagement_metrics: This is a measurement used to store the following engagement related metrics:
Running the Service
Using Docker
You can obtain or build a docker image for the Engagement Analytics microservice, check below the method of your preference. The image includes a base L4T image and the dependencies to run the engagement analytics microservice application. The image was developed and tested for NVIDIA JetPack 6.0. Once you get your image with either method proceed to Launch the container
Pre-build Image
Once you have obtained the engagement-analytics-service Docker image, you can install it in your Jetson with the following command:
docker load < engagement-analytics-service.tar.gz
Build Image
You can build the engagement analytics service image using the Dockerfile in the docker directory. First, we need to prepare the context directory for this build. You need to create a directory and include this repository and the remaining dependencies. The Dockerfile will look for all the packages in the context directory and copy them to the container.
After this, your context directory should look like this:
analytics-context/ ├── engagement-analytics └── rrms-utils
Then, build the container image with the following command:
docker build \ --network=host \ --tag ridgerun/engagement-analytics-service \ -f Dockerfile analytics-context/
Change analytics-context/ to your context's path and the tag to the name you want to give to the image.
Launch the container
You can ensure the image has been created successfully by running
docker images
You should get an entry showing the ridgerun/display-service image
nvidia@ubuntu:~$ docker images REPOSITORY TAG ridgerun/engagement-analytics-service latest
The container can be launched by running the following command:
docker run -it \ --network host \ --volume <path to directory containing your configuration file>:/configs \ -e INFLUXDB_TOKEN=<your influx db token> \ --name engagement-analytics-service \ ridgerun/engagement-analytics-service:latest \ --config-file /configs/<your configuration file name> \ --retry
Here we are creating a container called engagement-analytics-service that will start the engagement analytics service application (check Using Standalone Application), launching the server at 127.0.0.1 and port 5053. When the service starts, it will communicate with both redis and influxdb, so make sure both services are running.
After starting the service, you should see an entry with the engagement-analytics-service container:
nvidia@ubuntu:~$ docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 258b111a9721 ridgerun/engagement-analytics-service "engagement-analytics…" 2 hours ago Up 5 minutes engagement-analytics-servvice
Using Standalone Application
The engagement analytics service can also be used outside of the docker container. You can install it by running the following command from the project directory:
pip install .
Then you will have the service with the following options:
engagement-analytics --help
usage: engagement-analytics [-h] [--port PORT] [--host HOST] --config-file CONFIG_FILE [--retry]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--port PORT Port for server
--host HOST Server ip address
--config-file CONFIG_FILE
Configuration JSON file
--retry Keep trying to start the server if it fails initially
To start the service in address 127.0.0.1 and port 5053 just run:
engagement-analytics
If you want to serve in a different port or address, use the --port and --host options.
If you want to start with a configuration, you can use the --config-file argument to specify the path to your configuration.



